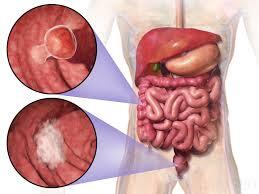
Colon cancer, also known as colorectal cancer, is one of the most common forms of cancer worldwide. It affects the colon or rectum, which are parts of the large intestine and plays a crucial role in the digestive system. Early detection is critical for improving survival rates and successful treatment outcomes. In this blog post, we’ll explore the symptoms of colon cancer, why they are often overlooked, and the importance of screening for early detection.
What is Colon Cancer?
Colon cancer begins in the colon, the longest part of the large intestine. It usually starts as small, benign clumps of cells called polyps that form on the inner lining of the colon. Over time, some of these polyps can develop into cancerous cells. The transformation from a benign polyp to cancer can take years, which is why regular screening is vital for early detection and prevention.
Colon cancer can be classified into different stages, ranging from Stage 0 (in situ) to Stage IV, based on the size, extent, and spread of the cancerous cells. Early-stage colon cancer often has a better prognosis and is more treatable compared to advanced stages where cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
Common Symptoms of Colon Cancer
Colon cancer symptoms can vary depending on the location and size of the tumor, as well as the stage of cancer. Unfortunately, many of these symptoms can be subtle or resemble those of other digestive conditions, leading to delays in diagnosis. Here are some common signs and symptoms to be aware of:
- Changes in Bowel Habits:
- Persistent changes in bowel habits, such as diarrhea, constipation, or a change in stool consistency, can be an early indicator of colon cancer. These changes may last for several weeks and are often not relieved by typical over-the-counter medications.
- Blood in the Stool:
- One of the most noticeable symptoms of colon cancer is blood in the stool. This may appear as bright red or dark, tarry stools. Blood in the stool should never be ignored, as it could indicate bleeding from the colon or rectum. However, not all blood in the stool is visible to the naked eye, and a test called fecal occult blood test (FOBT) can help detect hidden blood.
- Unexplained Weight Loss:
- Losing weight without trying is often a cause for concern. If you notice a significant and unexplained drop in weight, it could be due to colon cancer, which may interfere with the body’s ability to absorb nutrients or lead to decreased appetite.
- Abdominal Pain or Discomfort:
- Cramping, bloating, or persistent abdominal pain can be symptoms of colon cancer. The pain may be caused by a tumor obstructing the intestine or by the cancer spreading to other organs. It is essential to pay attention to pain that does not go away or worsens over time.
- Fatigue and Weakness:
- Chronic fatigue and a general feeling of weakness can be linked to anemia, a condition often caused by blood loss from colon cancer. Anemia can lead to a reduced oxygen supply to the body’s tissues, causing tiredness and lack of energy.
- Feeling that the Bowel Doesn’t Empty Completely:
- This sensation, also known as tenesmus, can occur when a tumor is located in the rectum. It can make an individual feel like they need to have a bowel movement even after they’ve just had one.
- Narrow or Thin Stools:
- If you notice a change in the diameter of your stool, with it becoming narrower than usual, it could indicate a blockage caused by a tumor in the colon.
Why Are Symptoms Often Overlooked?
Many of the symptoms associated with colon cancer are nonspecific and can be attributed to other, less severe conditions such as hemorrhoids, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), or dietary changes. This is why people often delay seeking medical advice, thinking that their symptoms are not serious. Additionally, some individuals may feel embarrassed discussing bowel issues with their healthcare providers, further delaying diagnosis.
The risk of colon cancer increases with age, particularly for individuals over the age of 50. However, recent studies have shown a worrying trend of increasing colon cancer cases among younger adults. This makes it even more important for everyone to be aware of the symptoms and seek medical advice if they notice any concerning changes.
The Importance of Screening and Early Detection
Regular screening for colon cancer can help detect the disease at an early stage when treatment is most effective. The American Cancer Society recommends that individuals at average risk of colon cancer begin screening at age 45. However, those with a family history of colon cancer or other risk factors may need to start earlier.
There are several screening methods available:
- Colonoscopy: This is the most comprehensive screening method, allowing doctors to examine the entire colon and rectum for polyps or cancer. If polyps are found, they can often be removed during the procedure.
- Stool Tests: These tests, such as the fecal immunochemical test (FIT) or the stool DNA test, look for signs of cancer or polyps in a stool sample.
- Flexible Sigmoidoscopy: This test examines the lower part of the colon and rectum for abnormalities. It’s less invasive than a colonoscopy but does not provide a full view of the colon.
- CT Colonography (Virtual Colonoscopy): This imaging test uses CT scans to create a detailed view of the colon and rectum.
Reducing Your Risk
While some risk factors for colon cancer, such as age and family history, cannot be changed, there are several lifestyle changes that can help reduce your risk:
- Diet and Exercise:
- A diet high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and low in red and processed meats, can help lower your risk. Regular physical activity and maintaining a healthy weight are also important.
- Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol:
- Smoking and heavy alcohol consumption are associated with an increased risk of colon cancer. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake can improve your overall health and reduce your cancer risk.
- Know Your Family History:
- If you have a family history of colon cancer or polyps, discuss it with your healthcare provider. You may need earlier or more frequent screenings.
- Be Proactive:
- If you experience any symptoms, even if they seem minor or are sporadic, consult with your healthcare provider. Early detection is key to successful treatment.
Conclusion
Colon cancer is a serious but often preventable disease. Awareness of the symptoms and the importance of regular screening can save lives. If you or someone you know is experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned, don’t wait—consult a healthcare professional. Early detection and treatment can make all the difference in the fight against colon cancer