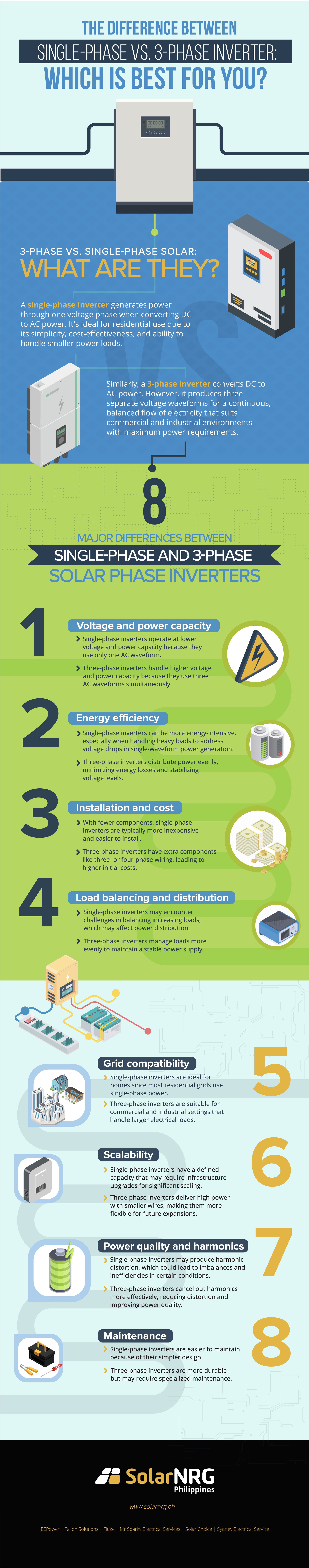
Harnessing solar energy starts with solar panels, but inverters play a key role in converting this energy into usable power. They transform the direct current (DC) electricity produced by solar panels into alternating current (AC), which powers homes and connects to the grid. When choosing a solar inverter, you’ll encounter two main types: single-phase and three-phase.
Single-phase inverters distribute electricity across one phase. These are ideal for residential systems and smaller energy needs, as they offer a simpler, cost-effective solution. However, they may not perform as efficiently for larger loads or commercial setups.
Three-phase inverters, on the other hand, distribute electricity across three phases, making them better suited for commercial and industrial applications. They handle larger loads more effectively and offer better energy efficiency, which is critical for high-demand systems.
Choosing between single-phase and three-phase depends on your energy requirements and property size. By selecting the right inverter, you can optimize your solar system’s performance, enhance energy efficiency, and lower electricity costs.
Explore the infographic below to gain a deeper understanding of how single-phase and three-phase inverters differ, and find the best fit for your solar needs.