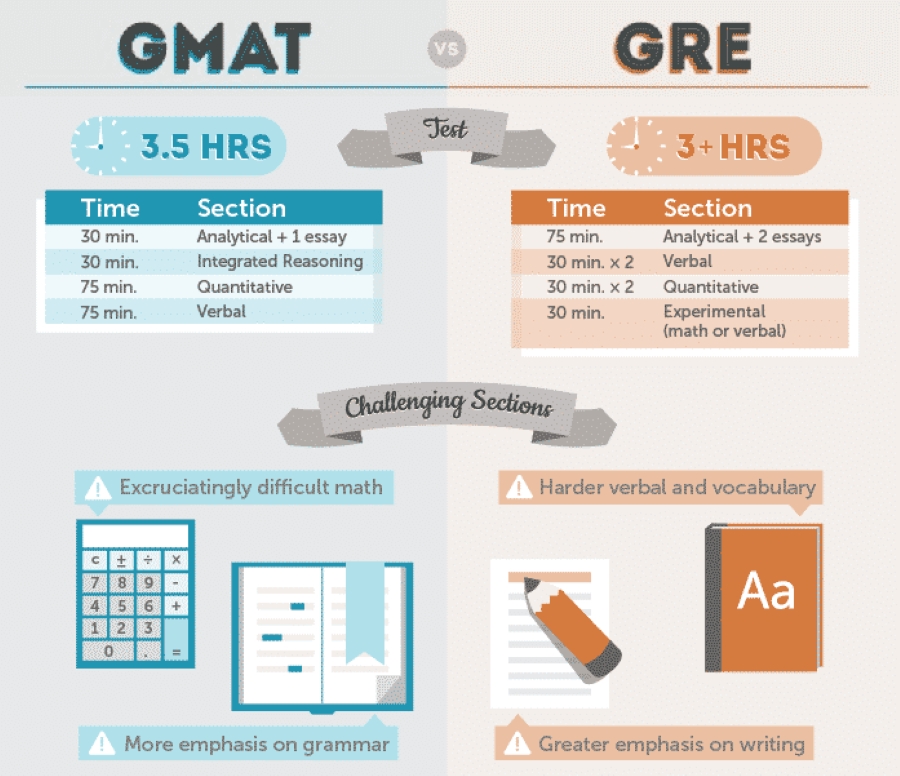
When deciding on the best test for graduate school admissions, many students weigh the Graduate Management Admission Test (GMAT) against the Graduate Record Examination (GRE). Both exams are widely accepted for graduate programs, yet they target different skills and have distinct structures, scoring systems, and use cases. This guide delves into the GMAT vs GRE key differences, offering insights into which exam may be better suited to your academic and professional goals.
Key Differences Between GMAT and GRE
The primary difference between the GMAT and GRE lies in their purposes and target audiences. While the GMAT is traditionally used for business school applications and focuses on analytical and quantitative skills, the GRE serves a broader range of disciplines, including sciences, humanities, and law.
Exam Comparison
- GMAT
- Primary Use: Business and Management Programs
- Accepted By: Business schools globally
- Skills Assessed: Analytical, reasoning, quantitative, and verbal skills
- GRE
- Primary Use: Various Graduate Programs across disciplines
- Accepted By: Graduate programs in diverse fields (sciences, humanities, law, etc.)
- Skills Assessed: General reading, math, and writing skills
The GRE’s versatility makes it ideal for applicants considering programs beyond business school, whereas the GMAT is more aligned with business and management studies.
Structure and Format Comparison
Both exams assess verbal, quantitative, and analytical writing skills but differ in format, structure, and time allocation.
GMAT Structure
The GMAT exam is divided into four sections, each focusing on a different skill set:
- Analytical Writing Assessment (AWA): 1 essay task (30 minutes)
- Integrated Reasoning (IR): 12 questions (30 minutes)
- Quantitative Reasoning: 31 questions (62 minutes)
- Verbal Reasoning: 36 questions (65 minutes)
The GMAT takes approximately 2 hours and 15 minutes to complete, not including optional breaks.
GRE Structure
The GRE is structured with three primary sections and an additional unscored section that does not affect the final score:
- Analytical Writing: 2 essay tasks (30 minutes each)
- Verbal Reasoning: 2 sections with 20 questions each (30 minutes per section)
- Quantitative Reasoning: 2 sections with 20 questions each (35 minutes per section)
The GRE generally lasts about 3 hours and 45 minutes, longer than the GMAT.
Timing and Duration
The GRE requires a longer commitment than the GMAT, as shown in the comparison below:
GMAT:
Total Duration: 2 hours 15 minutes
Analytical Writing: 30 minutes
Quantitative Sections: 62 minutes
Verbal Sections: 65 minutes
Breaks: One 10-minute break
GRE:
Total Duration: 3 hours 45 minutes
Analytical Writing: 60 minutes
Quantitative Sections: 70 minutes
Verbal Sections: 60 minutes
Breaks: Optional breaks between sections
This difference in duration can impact test-takers who may prefer a shorter, more intensive exam (GMAT) over a longer, more varied test (GRE).
Scoring Systems Explained
The GMAT and GRE score ranges are unique, and understanding these distinctions can help applicants interpret their scores and how schools assess them.
GMAT Scoring
- Total Score Range: 200–800
- Quantitative and Verbal Reasoning Scores: 6–51
- Analytical Writing Assessment (AWA): 0–6
- Integrated Reasoning: 1–8
The GMAT’s total score combines Quantitative and Verbal sections, which are emphasized in business school admissions.
GRE Scoring
- Total Score Range: 260–340
- Quantitative and Verbal Reasoning Scores: 130–170 each
- Analytical Writing: 0–6
The GRE’s scoring system does not aggregate Quantitative and Verbal scores, allowing a more distinct measurement of each skill.
Question Types and Difficulty Levels
The question types and difficulty levels of the GMAT and GRE differ significantly, particularly in how they assess quantitative and verbal skills.
GMAT Question Types
- Quantitative Reasoning: Problem-solving and data sufficiency questions without calculator use.
- Verbal Reasoning: Critical reasoning, sentence correction, and reading comprehension.
- Integrated Reasoning: Data interpretation tasks that require synthesizing information from graphs and tables.
The GMAT’s focus on business-related skills means it tends to have a more complex structure, emphasizing critical thinking over rote memorization.
GRE Question Types
- Quantitative Reasoning: Problem-solving and quantitative comparisons, with a calculator allowed.
- Verbal Reasoning: Text completion, sentence equivalence, and reading comprehension, often featuring challenging vocabulary.
The GRE’s verbal section has a greater emphasis on vocabulary and language complexity, which can be a barrier for non-native speakers.
Analytical Writing Assessment Comparison
The GMAT and GRE both assess writing skills through analytical writing tasks, but the format and focus vary:
- GMAT Analytical Writing: A single task to analyze an argument’s logic in 30 minutes.
- GRE Analytical Writing: Two tasks (one “issue” task and one “argument” task), each 30 minutes, allowing for a broader assessment of writing skills.
Cost Considerations
Test fees are a vital consideration, especially for students on a budget:
- GMAT Cost: Approximately $275, with additional fees for rescheduling and optional services.
- GRE Cost: Roughly $205, with similar fees for rescheduling and repeat exams.
Planning ahead can help students avoid unnecessary costs due to rescheduling or repeat attempts.
Which Exam Should You Choose?
The decision between the GMAT and GRE should align with your academic goals, strengths, and preferred study areas.
- Choose the GMAT if: You’re applying specifically to MBA or business-focused programs that value quantitative and analytical skills.
- Choose the GRE if: You’re considering a broader range of graduate programs, or if you prefer a test with a flexible structure and the use of a calculator in quantitative sections.
Selecting the right exam can enhance your application’s impact, demonstrating strengths aligned with your chosen program’s demands.
Conclusion
GMAT vs GRE both exams offer unique pathways to graduate school, yet they serve different academic and professional trajectories. By understanding each exam’s format, scoring, and suitability, students can make an informed decision that aligns with their ambitions and maximizes their chance for success in competitive graduate programs.